Drb_lecture_kinematics Of Curvilinear Translation j5j4a
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 445h4w
Overview 1s532p
& View Drb_lecture_kinematics Of Curvilinear Translation as PDF for free.
More details 6h715l
- Words: 551
- Pages: 4
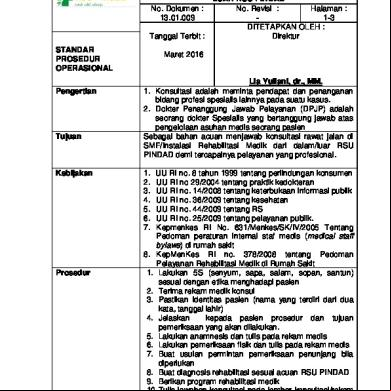
DYNAMICS OF RIGID BODIES Lecture Notes # 2 KINEMATICS OF CURVILINEAR MOTION Flight of Projectile (Air resistance neglected) Consider a motion of projectile in which such factors as wind velocity, air resistance and rotation of the earth, which affect the flight of projectile will be neglected then the flight path of the projectile will be the plane OABCD shown:
Equation of motion: 1. Horizontal component of velocity (constant throughout the entire flight of projectile): Vx = VocosΘ 2. Vertical component of velocity: Vy = VosinΘ - gt 3. Horizontal component of displacement: x = (VocosΘ) (t) 4. Vertical displacement: y = (VosinΘ) (t) – ½ gt2 Note: y is positive when the final position is higher than the initial position. y is negative when the final position is lower than the initial postion. 5. Velocity at any time: V =
Vx2 + Vy2
6. Slope at anytime: Engr. Jerome F. Famadico of 4 2nd Semester S.Y. 2013-2014
Page 1
DYNAMICS OF RIGID BODIES Lecture Notes # 2 tan Θ = Vy/Vx
7. Time to reach height (h) (max. height): t=
VosinΘ g
8. Maximum height (h): V 2sin2Θ h=o 2g 9. Time to reach R (range): t=
2VosinΘ g
10. To compute for the value of R: R =
Vo2sin2Θ g
11. To determine the equation of the flight: x2 y = xtanΘ – 1 g 2 V 2cos2Θ o Notes: 1. You may resolve the motion into x and y-components and use the formulas in rectilinear translation. 2. Θ is positive if the projectile is directed upward and negative if directed downward. 3. At any point D below the origin O, the sign of y is negative. 4. Vy is positive if directed upward and negative if directed downward. PRACTICE PROBLEMS:
Engr. Jerome F. Famadico of 4 2nd Semester S.Y. 2013-2014
Page 2
DYNAMICS OF RIGID BODIES Lecture Notes # 2 1. A stone is thrown from a hill at an angle of 60° with the horizontal on an initial velocity of 30 m/s. After hitting the level ground at the base of the hill, the stone has covered a horizontal distance of 150 m. How high is the hill? 2. A projectile is fired with an initial velocity of 60 m/s upward at an angle of 30° with the horizontal from a point 80 m above a level ground. What horizontal distance will it cover before it strikes the ground? 3. A ball is thrown from a tower 30 m. High above the ground with a velocity of 300 m/s directed at 20° from the horizontal. How long will the ball hit the ground?
4. A balloon is ascending at the rate of 10 kph and is being carried horizontally by a wind at 20 kph. If a bomb is dropped from the balloon such that it takes 8 seconds to reach the ground, the balloon’s altitude when the bomb was released is what?
5. A plane is flying horizontally 350 kph at an altitude of 420 m. At this instant, a bomb is released. How far horizontally from this point will the bomb hit the ground?
Engr. Jerome F. Famadico of 4 2nd Semester S.Y. 2013-2014
Page 3
DYNAMICS OF RIGID BODIES Lecture Notes # 2
Engr. Jerome F. Famadico of 4 2nd Semester S.Y. 2013-2014
Page 4
Equation of motion: 1. Horizontal component of velocity (constant throughout the entire flight of projectile): Vx = VocosΘ 2. Vertical component of velocity: Vy = VosinΘ - gt 3. Horizontal component of displacement: x = (VocosΘ) (t) 4. Vertical displacement: y = (VosinΘ) (t) – ½ gt2 Note: y is positive when the final position is higher than the initial position. y is negative when the final position is lower than the initial postion. 5. Velocity at any time: V =
Vx2 + Vy2
6. Slope at anytime: Engr. Jerome F. Famadico of 4 2nd Semester S.Y. 2013-2014
Page 1
DYNAMICS OF RIGID BODIES Lecture Notes # 2 tan Θ = Vy/Vx
7. Time to reach height (h) (max. height): t=
VosinΘ g
8. Maximum height (h): V 2sin2Θ h=o 2g 9. Time to reach R (range): t=
2VosinΘ g
10. To compute for the value of R: R =
Vo2sin2Θ g
11. To determine the equation of the flight: x2 y = xtanΘ – 1 g 2 V 2cos2Θ o Notes: 1. You may resolve the motion into x and y-components and use the formulas in rectilinear translation. 2. Θ is positive if the projectile is directed upward and negative if directed downward. 3. At any point D below the origin O, the sign of y is negative. 4. Vy is positive if directed upward and negative if directed downward. PRACTICE PROBLEMS:
Engr. Jerome F. Famadico of 4 2nd Semester S.Y. 2013-2014
Page 2
DYNAMICS OF RIGID BODIES Lecture Notes # 2 1. A stone is thrown from a hill at an angle of 60° with the horizontal on an initial velocity of 30 m/s. After hitting the level ground at the base of the hill, the stone has covered a horizontal distance of 150 m. How high is the hill? 2. A projectile is fired with an initial velocity of 60 m/s upward at an angle of 30° with the horizontal from a point 80 m above a level ground. What horizontal distance will it cover before it strikes the ground? 3. A ball is thrown from a tower 30 m. High above the ground with a velocity of 300 m/s directed at 20° from the horizontal. How long will the ball hit the ground?
4. A balloon is ascending at the rate of 10 kph and is being carried horizontally by a wind at 20 kph. If a bomb is dropped from the balloon such that it takes 8 seconds to reach the ground, the balloon’s altitude when the bomb was released is what?
5. A plane is flying horizontally 350 kph at an altitude of 420 m. At this instant, a bomb is released. How far horizontally from this point will the bomb hit the ground?
Engr. Jerome F. Famadico of 4 2nd Semester S.Y. 2013-2014
Page 3
DYNAMICS OF RIGID BODIES Lecture Notes # 2
Engr. Jerome F. Famadico of 4 2nd Semester S.Y. 2013-2014
Page 4