Bput Mba Syllabus 2016-17 | Mba Syllabus Of Bput 2016-2017 3s263g
This document was ed by and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. If you are author or own the copyright of this book, please report to us by using this report form. Report 445h4w
Overview 1s532p
& View Bput Mba Syllabus 2016-17 | Mba Syllabus Of Bput 2016-2017 as PDF for free.
More details 6h715l
- Words: 6,191
- Pages: 29
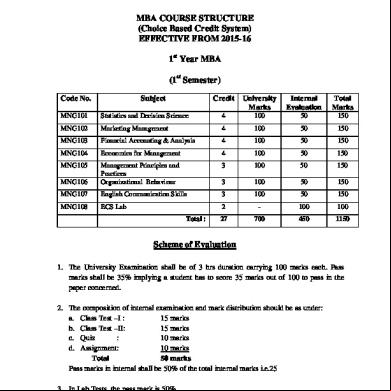
BIJU PATNAIK UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, ODISHA MBA COURSE STRUCTURE (Choice Based Credit System) EFFECTIVE FROM 2015-16 1st Year MBA (1st Semester) Code No.
Subject
Credit
University Marks
Internal Evaluation
Total Marks
MNG101
Statistics and Decision Science
4
100
50
150
MNG102
Marketing Management
4
100
50
150
MNG103
Financial ing & Analysis
4
100
50
150
MNG104
Economics for Management
4
100
50
150
MNG105
3
100
50
150
MNG106
Management Principles and Practices Organizational Behaviour
3
100
50
150
MNG107
English Communication Skills
3
100
50
150
MNG108
ECS Lab
2
-
100
100
27
700
450
1150
Total :
Scheme of Evaluation 1. The University Examination shall be of 3 hrs duration carrying 100 marks each. marks shall be 35% implying a student has to score 35 marks out of 100 to in the paper concerned. 2. The composition of internal examination and mark distribution should be as under: a. Class Test –I : 15 marks b. Class Test –II: 15 marks c. Quiz : 10 marks d. Assignment: 10 marks Total 50 marks marks in internal shall be 50% of the total internal marks i.e.25 3. In Lab Tests, the mark is 50%.
COURSE CONTENTS FOR MBA PROGRAMME UNDER CBCS PATTERN 1ST YEAR MBA Code: MNG -101 STATISTICS AND DECISION SCIENCE Credit - 4 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1. To lay an adequate theoretical foundation to study various applied fields in statistics and decision science. 2. To understand role of quantitative techniques in managerial decision making. 3. To understand applications of various quantitative techniques in managerial settings. Unit 01
Contents
Class hours Statistical Methods: Measures of central tendency and dispersion: 10 Standard Deviation, moments, measures of skewness and kurtosis. Simple Correlation, calculation of correlation coefficient, probable error, Rank correlation. Regression: Linear regression, calculation of regression coefficients, Multiple Regression Time series Model (Component, Uses, Moving Average Method, Least Square Method), Exponential Smoothing Techniques.
02
Probability: Concept, Addition, Conditional Probability Bay’s theorem, Probability Distributions: Normal and Binomial.
8
03
Decision Sciences & role of quantitative techniques. Linear Programming : Concept, Formulation & Graphical and Simplex Solution
8
Assignment Models: Concept, Flood’s Technique / Hungarian Method, applications including restricted & multiple assignments. Transportation Models: Concept, Formulation, Problem types: Balanced, Unbalanced, Minimization, Maximization Basic initial solution using North West Corner, Least Cost & VAM, and Optimal Solution using MODI.
04
Queuing Theory : Concept, Single Server (M/M/I, Infinite, FIFO) and Multi Server (M/M/C, Infinite, FIFO)
8
Markov Chains & Simulation Techniques: Markov chains: Applications related to management functional areas, Implications of Steady state Probabilities, Decision making based on the inferences Monte Carlo Simulation, Scope and limitations. 05
Decision Theory : Concept, Decision under risk (EMV) & uncertainty Game Theory : Concept, 2 zero sum game with dominance, Pure & Mixed Strategy
6
(Emphasis shall be laid on solving business related numerical problems in all the above modules)
Reference Books Quantitative Techniques for Management, Levine, Krehbiel, Berenson, Render Hanna, Pearson Quantitative Techniques in Management by N.D. Vohra Tata, McGraw Hill Quantitative Techniques-Davis.B, Oxford Operations Research by R. Pannerselvam, Prentice Hall Statistics for Business and Economics; R P Hooda, Vikas Operations Research by Nita Shah, Ravi Gor, Hardik Soni, PHI Business Statistics : J K Sharma
Code: MNG -102 MARKETING MANAGEMENT Credit- 4 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1. 2.
3.
To sensitize the students to the dynamic nature of Marketing Management. To expose students to a systematic frame work of marketing & implementations and to highlight need for different marketing approaches for services, goods, and for household consumers, organizational buyers. To introduce the concept of Marketing Mix as a framework for Marketing Decision making.
Unit
Contents
Class Hours
01
Definition & Functions of Marketing : Scope of Marketing, Core concepts of marketing such as Need, Want, Demand, Customer Value, Exchange, Customer Satisfaction, Customer Delight, Customer Loyalty, Marketing v/s Market, Selling versus Marketing, Concept of Marketing Myopia. 80: 20 Principle, Introduction to the Concept of Marketing Mix
6
02
Concept of Marketing Environment: Macro and Micro, Need for analyzing the Marketing Environment. .
10
Segmentation: Definition, Need for segmentation, Benefits of segmentation to marketers, Bases for market segmentation of consumer goods & industrial goods, Criteria for effective segmentation. Target Market: Concept of Target Market and criteria for selection of target market. Positioning: Concept of Differentiation & Positioning, Introduction to the concepts of Value Proposition & USP. Meaning & importance of consumer behavior, Comparison between Organizational Buying behavior and consumer buying behavior, Buying roles, Five steps buyer decision process. 03
Product : Meaning of product, Goods & Services Continuum, Classification of consumer products and industrial products, Product Mix: Length, Width, Depth and Consistency. New Product Development & Product Life Cycle : New Product Development Process: Idea Generation to commercialization. Product Life Cycle : Concept & Characteristics of Product Life Cycle. Relevance of PLC and Strategies across stages of the PLC. Branding: Introduction to Branding, Product Vs. Brand, Meaning of a brand, brand equity & brand elements. Packaging & Labeling : Meaning & role of Packaging & Labeling, Pricing Basics: Meaning, Importance and Factors Influencing pricing decisions. Setting the Price : Setting pricing objectives, Determining demand, Estimating costs, Analyzing competitors’ pricing, Selecting pricing method, Pricing approaches
9
8 04
Place: The Role of Marketing Channels: Channel functions & flows, channel levels. Channel Design Decisions: Analyzing customers’ desired service output levels, establishing objectives & constraints, Identifying & evaluating major channel alternatives. Channel Options: Introduction to Wholesaling, Retailing, Franchising, Direct marketing, E-Commerce Marketing Practices. Logistics Decisions: Order processing, Warehousing, Inventory, and Transportation. Promotion: The role of marketing communications in marketing effort. Communication Mix Elements : Introduction to Advertising, Sales Promotion, Personal Selling, Public Relations, Direct Marketing, Concept of Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC)
05
Marketing Planning & Control : Product Level Planning : Preparation & evaluation of a product level marketing plan, Nature & contents of Marketing Plans – Executive Summary, Situation Analysis, Marketing Strategy, Financials, Control. Contemporary topics: Viral marketing, Guerrilla marketing, societal marketing, Relationship marketing, green marketing, digital marketing, ( Concept only)
Reference Books Marketing: Baines, Fill and Page , Sinha , Oxford Marketing Management – Kotler, Keller, Koshy, Jha, Pearson, Marketing by Lamb Hair Sharma, Mc Daniel Cengage Learning Marketing Management, Ramaswamy & Namakumari, McGrawHill Marketing Management – K Karunakaran, Himalaya Publishing House Marketing Management – Text and Cases, Tapan K Panda, Excel Books Marketing Management Concept & Cases – S.A. Sherlekar Marketing Management – Karunakaran Marketing Management - Bose
7
Code : MNG 103 FINANCIAL ING AND ANALYSIS Credit- 4 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1. To familiarize the students with ing principles and acquaint them with ing mechanisms, process and systems so as to develop their skills of preparing financial statements. 2. To develop their ability to read annual reports and develop their skills to interpret financial statements. 3. To familiarize the students with different financial ing concepts affecting stakeholders Unit
Contents
01
Class Hours 6
Introduction to ing: What is ing? The need for ing, External and Internal End s of ing Information, ing concepts and conventions, ing cycle, ing Equations, Nature of GAAP, Need for ing Standards, Limitations of ing, Ethical Issues in ing, Basic Terminologies of ing. 8
02 Mechanics of ing: Introduction, Classification, Double Entry System, Preparing Journal, Subsidiary books, Ledger, preparation of Trial Balance. Preparation of Income statement and Balance Sheet.
03
(The students should familiarize with computerized ing and should be able to do a task relating to above through a software package). Corporate s: Share and Share Capital, Issue of Shares, Payment in installment, Buyback of shares, Debentures and Bonds. Understanding corporate Income statement and Balance Sheet as presented in the Annual Reports of companies.
8
04
Analysis and interpretation of Financing Statements:- Common size statement, Trend analysis, Ratio Analysis and Cash Flow Analysis as per AS – 3 (Revised).
8
05
The faculty has to pick up Annual Reports of at least 5 listed companies from different sectors and make groups to analyze the following aspects : - Financial analysis as reported by Auditors and Directors’ and Corporate Governance. - Basic EPS and Diluted EPS as per AS – 20 - State of Affairs through Valuation Ratios and Dupont analysis.
10
-
Consolidated statements of Cash Flows from the perspectives of lender, investor, Prospective employee and supplier to the company. Corporate disclosures in the Financial Statements and Annual Reports of past 5 years. Innovative Techniques of FSA
Reference Books Financial ing for Management; Paresh Shah, Oxford Financial ing A managerial Perspective-Bapat & Raitha, McGrawHill Financial ing for Managers-Sanjay Dhamija, Pearson Financial ing and Analysis- Athma, HPH Financial ing for Management, A.K.Bhattacharya Financial ing for Management, Narayanswamy
Code: MNG - 104 ECONOMICS FOR MANAGEMENT Credit – 4 Class Hours: 40 Objectives: 1. To lay an adequate theoretical foundation to study various applied fields in economics and management. 2. To demonstrate the application of economic theory to business decisions. 3. To develop a student’s ability to think analytically about the economic forces at work in society. 4. To develop a framework which the students may use to analyze the overall behavior of a modern mixed economy. Unit 01
02
Contents
Class hours. Relevance of economics for business decisions, Role of Managerial Economist 8 and Business decision making. Demand Analysis – individual market and firm demand, Determinants of demand, Elasticity measures and business decision making, Demand Estimation and demand Forecasting, Supply Analysis. Production functions: Single variable – Variable Proportions, two variables – isoquants, returns to scale; cost minimization and output maximization, Elasticity of substitution various cost concepts, cost functions and their empirical estimation, Economics of scale and economies of scope (simple numerical problems to be solved).
8
03
Market morphology, price and output determination under different market conditions: Perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, Descriptive pricing approaches: Full cost pricing, product pricing; Price skimming, penetration pricing, loss leader pricing, price bundling, Transfer pricing (simple numerical problems to be solved).
8
04
Macro economics, circular flow of income, the concepts of GDP, GNP, GDP deflator, concepts of consumption, saving, and investment, business cycle: Nature, phases, consequences and measures to solve the problems of business cycle. Inflation. Inter sectoral linkages, Macro aggregates and policy interrelation ships: Fiscal and Monetary Policies; Industrial Finance: Money market, Capital Market and institutional finance.
8
05
8
Reference Books Managerial Economics, Geetika, Ghosh, Raychoudhury, TMH Managerial Economics, Salvatre, Srivastava, Oxford Managerial Economics, Keat, Young, Banerjee, Pearson, Managerial Economics – Analysis of Managerial Decision Making, H L Ahuja, S. Chand Managerial Economics Theory and Applications, DM Mithani HPH Managerial Economics, PL Mehta Sultanchand & Co. Managerial Economics, DN. Dwivedi, Vikash
Code: MNG-105 MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICES Credit- 3 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4.
To explain the various concepts of management. To make the students understand the contemporary management practices To highlight professional challenges that managers face in various organization To enable the students to appreciate the emerging ideas and practices in the field of management.
Unit Contents 01
Class Hours
Introduction to Principles of Management 10
02
03
04 05
Basic Concepts : Definition of Management, Contribution of F.W. Taylor, Henri Fayol, Elton Mayo, Mary Parker Follet, Rensis Limert, Chestard Bernard, Douglas McGergor, Peter Drucker, Michael Porter and C.K. Prahlad. Approaches to Management : Scientific Approach, Systems Approach and Contingency Approach. Managerial Competencies : Communication, Team work, Planning and istrative, Strategic and Global Competencies. Organization : Formal and Informal, Line and Staff Relationship, Centralization Vs. Decentralization, Basic issues in Organizing, Work Specialization, Chain of Common Delegation, Span of Management, Organization Structure – Bases for Departmentation. Organizational Culture : Cultural Diversity, Multi Ethnic Workforce Organizing Knowledge Resource. Planning : Nature & Elements of Planning, Planning Types and Models, Planning in Learning Organizations, Types, Steps, MBO, MBE, Planning Premises. Decision Making : Risk and Uncertainty, Decision Trees, Decision making process, Models of Decision Making, Increasing Participation in Decision making, Decision-making creativity. Controlling : Process, Standards and Bench Marking – Co-ordinationPrinciples of Co-ordination-Inter-Dependence. Challenges in Management : Change Management – Timing of Change-Reaction to change-Planning organizational ChangeTechnological Change-Effective use of Communication Devices and IT.
10
8
5 7
Reference Books 1. Management, Robbins, Coulter & Vohra, Pearson. 2. Management: Text and Cases-VSP Rao, Excel Books 3. Essentials of Management-Koontz, 8/e, McGraw Hill 4. Management Theory & practice – Chandan J. S, Vikas Publishing House. 5. Management Theory & Practice Text & Cases – Subba Rao P & Hima Bindu, Himalaya Publication.
Code: MNG -106 ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOUR Credit- 3 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1.
To develop an understanding of the behavior of individuals and groups inside organizations To enhance skills in understanding and appreciating individuals, interpersonal, and group process for increased effectiveness both within and outside of organizations. To develop theoretical and practical insights and problem-solving capabilities for effectively managing the organizational processes.
2. 3.
Unit
Contents
Class Hours
01
Fundamentals of OB: Definition, scope and importance of OB, Relationship between OB and the individual, Evolution of OB, Theoretical framework (cognitive), behavioristic and social cognitive), Limitations of OB.
6
02
Attitude: Importance of attitude in an organization, Right Attitude, Components of attitude, Relationship between behavior and attitude, Developing Emotional intelligence at the workplace, Job attitude, Barriers to changing attitudes.
10
Personality and values: Definition and importance of Personality for performance, The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator and The Big Five personality model, Significant personality traits suitable to the workplace (personality and job – fit theory), Personality Tests and their practical applications. Perception: Meaning and concept of perception, Factors influencing perception, Selective perception, Attribution theory, Perceptual process, Social perception (stereotyping and halo effect). Motivation: Definition & Concept of Motive & Motivation, The Content Theories of Motivation (Maslow’s Need Hierarchy & Herzberg’s Two Factor model Theory), The Process Theories (Vroom’s expectancy Theory & Porter Lawler model), Contemporary Theories – Equity Theory of Work Motivation.
03
Foundations of Group Behavior: The Meaning of Group & Group behavior & Group Dynamics, Types of Groups, The Five – Stage Model of Group Development. Managing Teams: Why Work Teams, Work Teams in Organization, Developing Work Teams, Team Effectiveness & Team Building.
9
Leadership: Concept of Leadership, Styles of Leadership, Trait Approach Contingency Leadership Approach, Contemporary leadership, Meaning and significance of contemporary leadership, Concept of transformations leadership, Contemporary theories of leadership, Success stories of today’s Global and Indian leaders.
04
Organizational Culture : Meaning & Definition of Organizational Culture, creating & Sustaining Organizational Culture, Types of Culture (Strong vs. Weak Culture, Soft Vs. Hard Culture & Formal vs. Informal Culture), Creating Positive Organizational Culture, Concept of Workplace Spirituality.
05
Organizational Change : Meaning, Definition & Nature of Organizational Change, Types of Organizational Change, Forces that acts as stimulants to change. Implementing Organizational Change : How to overcome the Resistance to Change, Approaches to managing Organizational Change, Kurt Lewin’s-Three step model, Seven Stage model of Change & Kotter’s Eight-Step plan for Implementing Change, Leading the Change Process, Facilitating Change, Dealing with Individual & Group Resistance, Intervention Strategies for Facilitating Organizational Change, Methods of Implementing Organizational Change, Developing a Learning Organization.
Reference Books 1. Understanding Organizational Behaviour, Parek, Oxford 2. Organizational Behaviour, Robbins, Judge, Sanghi, Pearson. 3. Organizational Behaviour, K. Awathappa,HPH. 4. Organizational Behaviour, VSP Rao, Excel 5..Introduction to Organizational Behaviour, Moorhead, Griffin, Cengage. 6. Organizational Behaviour, Hitt, Miller, Colella, Wiley
8
7
Code: MNG -107 ENGLISH COMMUNICATION SKILLS Credit- 3 Class Hours - 30 Objectives: 1. To develop the communication skills of the students 2. To encourage the students to make correct usage of English with an emphasis on Listening, Speaking, Reading and Writing skills 3. To familiarize the students with professional communication. Unit
01
Contents
Basics of Communication
Class Hours 6
Importance of communication ,Communication elements and process, General communication and business communication, Information Gap principle, Turn-taking, Awareness of Filters & Barriers & Strategies for overcoming them, Verbal and non‐verbal communication, Principles of effective communication, Communication network in an organization Communication through English 02
6 The importance of communication through English at the present time, Plain English. Bias free English, Formal / Informal language use in appropriate contexts. The Sounds of English: Vowels and consonants, IPA symbols, Syllables, Stress and Intonation.
03
Major Language Skills (LSRW) Listening: Importance, Active & ive listening, barriers, strategies for improving listening skills. Speaking: Characteristics of Effective Speech-Clear articulation; Rate of speaking; Voice quality; Eye ; Relevance of content for the audience Reading: D e v e l o p i n g reading skills of skimming and scanning; predicting, guessing the meaning of unfamiliar words, inferring; reading critically, taking notes. Writing: the characteristics of effective writing, clear organization and structuring of ideas, summarizing, clarity of language, stylistic variation, précis writing, paragraph writing.
6
04
05
Functional English Grammar English Verbs, Tenses, Subject-verb concord, Negation, Interrogation Parallel structure, Modifiers, Clause and its types, Punctuation.
6
Conversations, Dialogues and Debates: Purpose and features of good conversations, tips for improving conversations, situational dialogues and role plays, Features of a good debate and how to prepare for it.
6
Reference Books 1.Communication Skills , Sanjay Kumar & Pushpa Lata, Oxford 2.An introduction to Professional English and Soft Skills: Das et al, BPUT Text Book. CUP. 3.Better English Pronunciation, J.D.O. Connor (Cambridge) 4.A University Grammar of English, Quirk et al, Pearson 5.Business communication, C.S.G. Krishnamacharyulu & Lalitha Ramakrishnan
Code: MNG -108 ENGLISH COMMUNICATION SKILLS - LAB Credit- 2 Class Hours - 20 1. 2. 3.
4.
Role plays for practice in effective use of body language, paralanguage and spatial communication. Phonemic transcription using IPA symbols. Syllable division and stress marking Listening exercises Listening with a focus on pronunciation: segmental sounds, stress, weak forms, intonation. Listening for meaning: listening to a short talk / news bulletin. Taking notes from a lecture/speech. Speaking exercises
5.
Pronunciation practice (for accent neutralization), Practicing word stress, and intonation. Practice of greetings and other functional expressions. Giving a short speech on a topic of interest. Participate in debates. Reading exercises Note making after reading a text, showing the main idea and s upporting ideas and the relationship between them.
6.
Writing exercises Practice in writing paragraphs , Précis writing
7.
Practice exercises on the common grammatical errors. Remedial measures to focus on correct use of English verbs, sentence structures, clause-types, Interrogation and parallel structures.
Lab Tests: 1st Lab test, 30 marks.(Listening, Speaking, Non-verbal communication) 2nd Lab test, 40 marks (Reading, Pronunciation, Grammar & Vocabulary) 3rd Lab test 30 marks (Writing) Suggested Readings: 1. A practical Course in Spoken English, Gangal, PHI 2. English Language Laboratories, Nira Konar, PHI
MBA Structure (Choice Based Credit System) EFFECTIVE FROM 2015-16 1st Year MBA 1st Semester Code No.
Subjects
Credit
University Marks
Internal
Total Marks
MNG 101 MNG 102
Statistics and Decision Science Marketing Management
4 4
100 100
50 50
150 150
MNG 103
Financial ing and Analysis
4
100
50
150
MNG 104
Economics for Management
4
100
50
150
MNG 105
Management Principles and Practices
3
100
50
150
MNG 106
Organizational Behaviour
3
100
50
150
MNG 107
English Communication Skills
3
100
50
150
MNG 108
ECS Lab
2
-
100
100
27
700
450
1150
Credit
University Marks
Internal
Total Marks
Total
2nd Semester Code No.
Subjects
MNG 201
Business Research Methods
3
100
50
150
MNG 202
Business, Environment and Society
3
100
50
150
MNG 203
Financial Management
4
100
50
150
MNG 204
Banking and Insurance
3
100
50
150
MNG 205
Operations Management
4
100
50
150
MNG 206
Human Resource Management
4
100
50
150
MNG 207
Managerial Communication
2
100
50
150
MNG 208
Managerial Communications Skill Lab
2
-
100
100
MNG 209
Business Data Analysis Lab
2
-
100
100
27
700
550
1250
Total
Summer Vacation: Summer Training Program for 4 to 8 weeks in identified sector.
2nd Year MBA 3rd Semester Code No.
Subjects
Credit
University Marks
Internal
Total Marks
MNG 301
Cost and Management ing
3
100
50
150
MNG 302
Business Law
3
100
50
150
MNG 303
Start ups and Business Incubation
3
100
50
150
MNG 304
Elective-I (Major)
4
100
50
150
MNG 305
Elective-II (Major)
4
100
50
150
MNG 306
Elective-III (Major)
4
100
50
150
MNG 307
Elective-IV (Minor)
4
100
50
150
MNG 308
Summer Internship
3
100
-
100
28
800
350
1150
Credit
University Marks
Internal
Total Marks
Total
4th Semester Code No.
Subjects
MNG 401
Strategic Management
3
100
50
150
MNG 402
Elective-V (Major)
4
100
50
150
MNG 403
Elective-VI (Minor)
4
100
50
150
MNG 404
Open Elective
3
100
50
150
MNG 405
Project Work on Business Management
4
-
100
100
18
400
300
700
Total
Each student shall undergo a project work in a business enterprise for 2 months during 4th Semester.
Detailed Syllabus for 2nd Semester, MBA MNG-201 BUSINESS RESEARCH METHODS Credit-3 Class Hours-40 Objectives: To equip the students with the basic understanding of the research methodology in changing business scenario. to provide an insight into the application of dynamic analytical techniques to face the stormy challenges, aimed at fulfilling the objective of business decision making. Unit Contents Class Hours Introduction to BRM: 01 Meaning and significance of research. Importance of scientific research in business decision making. 8 Types of research and research process. Identification of research problem and formulation of hypothesis. Research Designs. Measurement and Data Collection. 02 Primary data Secondary data 8 Design of questionnaire Sampling fundamentals and sample designs. Measurement and Scaling Techniques Data Processing Data Analysis – I: 03 Hypothesis testing Z-test, t-test,F-test, chi-square test. 12 Analysis of variance. Non-parametric Test – Sign Test, Run test, Krushall – Wallis test Data Analysis – II: 04 Factor analysis. Multiple Regressions Analysis. 12 Discriminant Analysis (Concept) Report writing and presentation: Research Report, Types and significance Structure of research report Presentation of report. 05 Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory Practical Aspect : Students are expected to use the 40 days trial version of relevant software package to learn the following :-
(I) Draw frequencies, bar charts, histogram. (ii) Creating and editing graphs and charts. (iii) Bi-variate correlation. (iv) The t-test procedure. (v) Non-parametric Tests : Chi-square Test. (vi) One way ANOVA Procedure. (vii) Simple Regression, Multiple Regression, Reliability Analysis, Factor Analysis. Reference Books: 1. Research Methodology, by Deepak Chawla / Neena Sandhi (Vikas) 2. BRM by Zikmund / Babin / Carr / Adhikari / Griffin (Cengage) 3. Research Methodology, by V. Upadade &A. Shende (S. Chand) 4. Business Research Methods by Naval Bajpai, Person 5. Business Research Method by Cooper et.al, McGraw Hill 6. Research Methodology by Khatua and Majhi, HPH.
MNG 202 BUSINESS, ENVIRONMENT & SOCIETY Credit-3 Class Hours-30 Objectives: 1. To analyse different issues of environment and measures to control those. 2. To enrich the students’ understanding of current scenario of society and related problems. 3. To direct the attention of students towards activities meant for betterment of the society. 4. To make the students understand the initiatives of corporates to pay back to the society and how they derive a social return in long run. Unit Contents Class Hours Concept of business environment: 01 Business Environment : Classification (Internal; External :- Micro &Macro 7 – Economic, Political-legal, Socio-Cultural, Techical, Democraphic, Natural International), Technics of Analysis and Diagnosis ((SWOT, ETOP, Forcasting; The New Economic Policy (LPG); National and State Level Industrial Polices. Environmental Issues and Controlling Measures: 02 Cause, effect and control measures of pollution (Air, Water, Soil, Marine, 7 Noise, Nuclear hazzards); Cause, effect and control measures of urban and industrial wastes; Managing Natural Disasters (flood, earthquake, cyclone and landslides) and Man made Disasters. Contemporary Social issues: 03 Polpulation explosion; Poverty-cause, effect and control measures; 7 Unemployment; Dowry, Domestic violance; Child labour; Terrorism; Cyber crime; Corruption in public sphere; Ineuality of caste and gender; Issues related to religious, ethnic, regional,minority, backward class, dalits in India. Corporate Social Responsibility(CSR): 04 Concept,Dimensions of CSR, Models of CSR: Philanthropic, Europian and Indian; CSR initiatives by public and private sector organizations in 9 India; Social audit; Social Return on Investment(SROI)- Concept, steps to measure, Implications, Community Welfare, Elevated Executives. 05 The above contents need to be discussed in the class room through field studies, case analysis and seminar presentations etc.
Reference Books: 1.Environmental Studies, Bosak, Pearson 2.Indian Social Problems- A Sociological Prespective, Rao CNS, S Chand 3..Social Problems in India, Ahuja R, Rawat Publishers 4. Environmental Studies, Asthana / Asthana – S. Chand
5. Environmental Management – Pandey Vikash Publication. 6. Business Ethics – Murthy Himalaya Puhlishing House 7.Business Environment, Paleri, Cengage MNG-203 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT CREDIT: 4 CLASS HOURS: 40 Objective :This course provides students with concepts, techniques and tools to study, analyze and improve their knowledge on financial management practices of an organization
Unit 01
02
03
04
Contents Foundations of Finance Nature &Scope. Organization of Financial Functions. Emerging role of FMs in India and in Global context. Financial Goal.Agency problems. Time value of money. Risk and Return concepts, Risk and return in a single asset and two assets portfolio. Investment Decisions. Capital Budgeting: Features, types and Techniques of capital budgeting decision. Cost of Capital. Financing &Dividend Decision: Operating Leverage, Financial Leverage. Capital structure. Theory and Policy. Sources of Long term finance, Dividend Theory.Dividend Policy. Current Assets Management: Working Capital concepts, Policies, estimation, factors affecting working capital, Sources of financing Working Capital, Management of cash : Cash budget, Management of collections and disbursement, Investment of Surplus cash ; Management of Receivables : of Credit, Credit Policy decision ; Management of Inventory : Techniques of Inventory planning and control.
05 Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory Books : 1. Essentials of Financial Management, IM Pandey, Vikas 2. Financial Management, Khan & Jain, McGraw Hill, 3. Financial Management, Srivastav & Misra, Oxford. 4. Financial Management, G Sudarsan Reddy, HPH 5. Financial Management, Kapil, Pearson 6. Financial Management – Tulsian (S Chand) 7. Fundamentals of Financial Management, Brigham, Cengage
Class Hours 10
10
10
10
MNG-204 BANKING AND INSURANCE Credit-3 Class Hours-30 Objectives: To equip students with a thorough understanding of need and importance of banking and insurance in the modern day life. To make students understand the basic legal provisions necessary for banks in India to operate. To summarize methods of handling risk, identify and explain features of insurance, its advantages and dis advantages. Unit Contents Class Hours Overview of Banking 01 Evolution of Banking, Structure andTypes of Banks (Commercial Bank, Cooperative Bank, Payment Bank, Small Banks), Roles of Banks (viz. 6 Intermediation),Payment system, Financial services), Banking Services, Banking Products – Deposit and Loan products, Payment products. EBanking, RTGS and NEFT. Banking Regulations and Financial Stability 02 Need and importance of Banking regulation in India, Banking Regulation Act,1949; KYC and AML guidelines, Banking Fraud, Banking Code, 7 BASEL norms, SARFAESI ACT, ARCs,Banking ombudsman scheme; policies with respect to priority sector and MSMEs. Basics of Insurance 03 Basic principles of business of insurance, Types of insurance: Life and Nonlife Insurance, Re Insurance. Principles governing marketing of 10 insurance products; Insurance regulations and role of IRDA. Extension of insurance to Niche areas: Pension plans, Bancassurance, ULIPs, TPA, Micro Insurance, Insurance Inclusion. Insurance Risk and Claims Management 04 Risk and Uncertainty, Risks associated with business of insurance i.e . pure risk, financial risk, fundamental risk. Classification of pure risk, 7 overlapping risks; Rules of Risk management, Risk management techniques, Risk management process, Underwriting. Claims settlement procedure for Life insurance, Motor insurance and HealthInsurance. 05
Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory
Reference Books: 1. Banking Theory, Law and Practice – Gordon – Natarajan, HPH 2. Banking and Insurance – Mohapatra and Acharya, Pearson 3. Insurance and Risk Management, P.K. Gupta – HPH 4. RISK Management and Insurance – Triechmann, Cengage
5. Banking Theory &Practice – Shekhar / Shekhar (Vikas) 6. Banking Law and Practice – S. Mishra (S Chand) 7. RBI Bulletin 2013, 2014 8. National Insurance Academy publications
MNG 205 OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Credit: 4 Class Hours-40 Objective: 1.
To understand the concepts, principles, problems, and practices of Operations Management.
2.
To understand the importance of an effective operations strategy in an organization.
3.
To understand the various production and operations design decisions and how they relate to the overall strategies of organizations.
Module
Contents
Overview of Operations Management– Operations in Manufacturing and Services, Responsibility of Operations Manager, Operations Strategy and Competitiveness, Process Analysis, Manufacturing Process and Service Process Selection and Design, Job Design and Work Measurement. Facility Location, Layout &Capacity Planning– Locational Factors, II Techniques; Factor Rating Method, Centroid Method; Facility Layout, Process Layout, Product Layout and Line Balancing, Fixed Position Layout, Service Operations Layout, Modern Layouts, Types of Capacity, Capacity Planning &Strategies, Economics of Scale and Scope. Aggregate Planning, Scheduling &Project Management– III Aggregate Planning; Relevant Cost and Strategies, Scheduling; Priority Rules and Techniques, Gantt Chart; JIT; Project Management, PERT/M- Network Diagram and Critical Path, Slack &Float. Quality Managementand Supply Chain Management– Concept of IV Supply Chain Management; Concept of Quality; Design of Quality Control System, Statistical Quality Control, Types of Control Chart – X Chart, R Chart, P Chart, TQM (Total Quality Management) Concepts, Introduction to ISO 9000 &14000 Standards. V Case Studies – Emphasis shall be laid on case studies and solving business related numerical problems in all the above modules. Reference Books:
Class Hours
I
10
10
10
10
1. Operations Management, Chase et.al – Tata McGraw Hill. 2 Operations Management, Meenakhi Kumari, Cengage 3. Production and Operations Management, Kaniska Bedi, OXFORD 4. Production and Operations Management, K. Aswathappa, K. Shridhar Bhat, HPH 5. Production &Operations Management, SP Singh, Vikas Publication 6. Operations Management, Heizer and Render, Pearson MNG-206 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Credit-4 Class Hours-40 Objectives: 1. To introduce and explain different phenomenon of Human Resource Management (HRM). 2. To enrich the students’ understanding on HRM , which may enable them to implement the concepts in the workplace. 3. To direct the attention of students towards some of the emerging concepts of HRM. Unit Contents Class Hours 01 Concept, Definitions and Objectives of Human Resource Management(HRM); Functions of HRM; Process of HRM; Evolution of HRM; Strategic HRM and its role in the organization; Human Resource 10 Planning(HRP):Meaning and Process, Job analysis: Job description and Job specification; Recruitment: Meaning, Sources, Process and Yield; Selection: Meaning and Process, Tests and Interviews, Induction and Socialization. 02 Performance Appraisal: Meaning, Objective, Process and Methods; Potential Appraisal; Biases in performance appraisal; Methods of job evaluation; Meaning of Compensation; Types of compensation; Types of 10 wages and theories; Wage differentials; Pay structure, Wage Law in India, Executive Compensation. 03 Concepts of Career, Career planning process, Career Stages; Training &Development: Concept, Training need analysis and Methods of training 10 (on-the-job and off-the-job training), Evaluation of Training effectiveness; Concepts of Promotion, Transfer and Separation. 04 Industrial Relations (IR): Concept and Approaches to IR, John T. Dunlop’s System Theory of IR, Positive and Negative IR, Role of State in IR; Trade Unions: Concept and Registration; Structure and Functions of Trade Union, International HRM: Definitions and Approaches, Concepts of Expatriate, Parent country National (PCN), Host Country National 10 (HCN)and Third Country National (TCN). Challenges of HRM in dynamic business environment; Ethical issues in HRM HR Outsourcing; Employee Engagement; Organization Citizenship Behaviour(OCB), Talent Management, Competency Mapping. 05 Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory
Reference Books: 1.HRM Text &Cases, Aswathappa,TMH. 2. Personnel &Human Resource Management, P.Subba Rao,HPH 3. Human Resource Management,Jyoyi,Venkates, Oxford 4. HR, Denisi and Sarkar, Cengage. 5. Human Resource Management (Seema Sanghi (Vikas) 6. Human Resource Management – S.S. Khanka – (S. Chand) 7. Human Resource Management – Dessler and Verkky, Pearson
MNG- 207 MANAGERIAL COMMUNICATION CREDIT - 2 CLASS HOURS: 30 Objectives: To develop the communication skills and soft skills of the students To enhance the ability of the students to participate in group discussions and personal interviews Unit Contents Class Hours 1
Introduction to Managerial Communication
7
1.1. Communication challenges in today’s work place: Advances in technology; Culturally diverse workforce; Team-based organizational Settings. 1.2 Effective Business Presentations: Importance in managerial communication; Planning, Preparing, Organizing, Rehearsing, and Delivering Oral presentations, Handling Questions; Power Point Presentation 2
Introduction to Managerial writing
7
2.1. Business letters: routine and persuasive letters, bad news letters, sales letters, job application letters. 2.2. Writing CVs. 2.3. Memos, notices, circulars, emails. 2.4 Business reports and proposals. 3
Group Communication 3.1. Business Meeting: Planning a meeting; Drafting a Notice-cumAgenda; Role of the Chairperson and other participants; preparing the
8
Minutes of a meeting. 3.2. Group discussion: Types; Do's and Don'ts of GD; Guidelines for Effective Group Discussions.. 3.3Types of managerial speeches: Speech of Introduction, speech of thanks, occasional speech, and theme speech. 4
Soft Skills
8
4.1. Communication skills and Soft Skills. 4.2. Mastering the art of giving interviews, Types of interviews, Planning and Preparing for a Job Interview; Frequently Asked Questions in a Job Interview; Stages of an Interview; Important Nonverbal Aspects; Strategies for success in Job Interviews. 4.3. Business and social etiquettes. 5
Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory
Recommended Books: 1. Business Communication- concepts, cases & applications,Chaturvedi & Chaturvedi,
Pearson
2. Business Communication, Meenakshi Raman & Prakash Singh, Oxford 3. Communication for Management, Urmila Rai and S M Rai, HPH 4. Business and Managerial Communication, Sengupta, PHI 5. Business Communication for Managers, P. Mehra, Pearson 6. BCOM 2nd Edition, Lehman and Sinha, Cengage 7. Soft Skills K Alex, S Chand 8. Business Communication, Kalia and Agarwal, Wiley
Managerial Communication Skills (Lab) Credit – 2 Hours - 30 Unit
Contents
1
Managerial Writing: Business letters, ment, Preparing Press Releases, Press Notes, Writing themespeeches, Speeches of thanks.
2
Group Team / Communications: Preparing for GDs, Interviews, Writing CVs and Resumes, Internal communications for employee engagement.
Sessions (in Hours) 6 12
Business Etiquette. 3
4.
Corporate Communications: Notices, Agenda, Board Room Behaviour, Minutes, Exercises in Corporate writing, Preparing Presentation, Making presentations before the top management.
6
Learning Emotional Skills: Emotional Skills and your personality, Interpersonal relations. Know your EQ. EQ Tests.
6
30 Hours Conducting Tests : 1.
There shall be two lab tests carrying 30 marks each and another carrying 40 marks.
2.
The faculty concerned shall design the tests on topics prescribed in the syllabus.
Recommended Books : 1.
English Language Lab, Nira Kanor, PHI
2.
Guide to Managerial Communication, Mary Munter, Pearson
3.
Cengage Learning India, English Language Communication Skill – Lab Manual
4.
Soft Skills for Everyone, Butterfield, Cengage
5.
Campus to corporates, Sage Publication
Conducting Tests: 1.
There shall be two lab tests carrying 30 marks each and another carrying 40 marks.
2.
The faculty concerned shall design the tests on topics prescribed in the syllabus.
Recommended Books: 1. English Language Lab, Nira Kanor, PHI 2. Guide to managerial Communication, Mary Munter, Pearson 3. Cengage Learning India, English Language Communication Skill – Lab manual 4. Soft Skills for every everyone, Butterfield, Cengage
MNG 209 Business Data Analysis Laboratory
Credit: 2 Hours : 30 Teaching Scheme: Laboratory 4Hrs/Week Prerequisites: Basic Mathematics and Management Objective:To Make students familiar with business data analysis,retrieval using computer for research and report generation. Session 1
Contents An introduction to creating and formatting worksheets
Hours 2
The session includes : Insert and delete worksheets;Copy, reposition, copy and move, rename, grouping and applying coloring to worksheet tabs 2
Applying formulas and functions
4
Create formulas This session includes :
Use of basic operators
Revision of formulas
Enforce precedence of operation This session includes:
3
order of evaluation
precedence using parentheses
Precedence of operators for percent vs exponential
Apply cell reference in formulas
2
This session includes:
4
Relative
Absolute
Applying conditional logic in a formula This session includes:
Create formula with values that match your conditions
Edit defined conditions in a formula
Use a series of conditional logic values in a formula
2
5
Apply name ranges in a formulas.
2
This session includes: 6
Define,edit and rename a named range
Apply cell ranges in formulas.
2
This session includes :
7
Enter a cell range destination in the formula bar
Define a cell range using the mouse
Define a cell range using a keyboard shortcut
Presenting Data Visually
2
This session includes :
Create charts based on worksheet data. Introduction to Query Language
8
4
SQL DDL commands This session includes:
Creating tables
Creating table with constraints
Altering tables
SQL DML commands This session includes
Inserting data into tables
Updating data into tables
Deleting data from tables
9
Getting data using Query Use of select statement to create data queries
2
10
Advance Query 1
4
Use of SQL functions (aggregate functions,group functions etc.) Advance Query 2
Use of s and sub queries
11
Lab. Test 1 (Spread sheet - 50 marks)
2
12
Lab. Test 2 (Query language - 50 marks)
2
Total no. of Lab Hours = 30
Note: Lab activities will be done using only open source spread sheet and open source database like My SQL Course Outcome: After taking this course the student will be able to:
Design spreadsheets and data base tables for data analysis
Analyse the data and prepare graphical reports
Subject
Credit
University Marks
Internal Evaluation
Total Marks
MNG101
Statistics and Decision Science
4
100
50
150
MNG102
Marketing Management
4
100
50
150
MNG103
Financial ing & Analysis
4
100
50
150
MNG104
Economics for Management
4
100
50
150
MNG105
3
100
50
150
MNG106
Management Principles and Practices Organizational Behaviour
3
100
50
150
MNG107
English Communication Skills
3
100
50
150
MNG108
ECS Lab
2
-
100
100
27
700
450
1150
Total :
Scheme of Evaluation 1. The University Examination shall be of 3 hrs duration carrying 100 marks each. marks shall be 35% implying a student has to score 35 marks out of 100 to in the paper concerned. 2. The composition of internal examination and mark distribution should be as under: a. Class Test –I : 15 marks b. Class Test –II: 15 marks c. Quiz : 10 marks d. Assignment: 10 marks Total 50 marks marks in internal shall be 50% of the total internal marks i.e.25 3. In Lab Tests, the mark is 50%.
COURSE CONTENTS FOR MBA PROGRAMME UNDER CBCS PATTERN 1ST YEAR MBA Code: MNG -101 STATISTICS AND DECISION SCIENCE Credit - 4 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1. To lay an adequate theoretical foundation to study various applied fields in statistics and decision science. 2. To understand role of quantitative techniques in managerial decision making. 3. To understand applications of various quantitative techniques in managerial settings. Unit 01
Contents
Class hours Statistical Methods: Measures of central tendency and dispersion: 10 Standard Deviation, moments, measures of skewness and kurtosis. Simple Correlation, calculation of correlation coefficient, probable error, Rank correlation. Regression: Linear regression, calculation of regression coefficients, Multiple Regression Time series Model (Component, Uses, Moving Average Method, Least Square Method), Exponential Smoothing Techniques.
02
Probability: Concept, Addition, Conditional Probability Bay’s theorem, Probability Distributions: Normal and Binomial.
8
03
Decision Sciences & role of quantitative techniques. Linear Programming : Concept, Formulation & Graphical and Simplex Solution
8
Assignment Models: Concept, Flood’s Technique / Hungarian Method, applications including restricted & multiple assignments. Transportation Models: Concept, Formulation, Problem types: Balanced, Unbalanced, Minimization, Maximization Basic initial solution using North West Corner, Least Cost & VAM, and Optimal Solution using MODI.
04
Queuing Theory : Concept, Single Server (M/M/I, Infinite, FIFO) and Multi Server (M/M/C, Infinite, FIFO)
8
Markov Chains & Simulation Techniques: Markov chains: Applications related to management functional areas, Implications of Steady state Probabilities, Decision making based on the inferences Monte Carlo Simulation, Scope and limitations. 05
Decision Theory : Concept, Decision under risk (EMV) & uncertainty Game Theory : Concept, 2 zero sum game with dominance, Pure & Mixed Strategy
6
(Emphasis shall be laid on solving business related numerical problems in all the above modules)
Reference Books Quantitative Techniques for Management, Levine, Krehbiel, Berenson, Render Hanna, Pearson Quantitative Techniques in Management by N.D. Vohra Tata, McGraw Hill Quantitative Techniques-Davis.B, Oxford Operations Research by R. Pannerselvam, Prentice Hall Statistics for Business and Economics; R P Hooda, Vikas Operations Research by Nita Shah, Ravi Gor, Hardik Soni, PHI Business Statistics : J K Sharma
Code: MNG -102 MARKETING MANAGEMENT Credit- 4 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1. 2.
3.
To sensitize the students to the dynamic nature of Marketing Management. To expose students to a systematic frame work of marketing & implementations and to highlight need for different marketing approaches for services, goods, and for household consumers, organizational buyers. To introduce the concept of Marketing Mix as a framework for Marketing Decision making.
Unit
Contents
Class Hours
01
Definition & Functions of Marketing : Scope of Marketing, Core concepts of marketing such as Need, Want, Demand, Customer Value, Exchange, Customer Satisfaction, Customer Delight, Customer Loyalty, Marketing v/s Market, Selling versus Marketing, Concept of Marketing Myopia. 80: 20 Principle, Introduction to the Concept of Marketing Mix
6
02
Concept of Marketing Environment: Macro and Micro, Need for analyzing the Marketing Environment. .
10
Segmentation: Definition, Need for segmentation, Benefits of segmentation to marketers, Bases for market segmentation of consumer goods & industrial goods, Criteria for effective segmentation. Target Market: Concept of Target Market and criteria for selection of target market. Positioning: Concept of Differentiation & Positioning, Introduction to the concepts of Value Proposition & USP. Meaning & importance of consumer behavior, Comparison between Organizational Buying behavior and consumer buying behavior, Buying roles, Five steps buyer decision process. 03
Product : Meaning of product, Goods & Services Continuum, Classification of consumer products and industrial products, Product Mix: Length, Width, Depth and Consistency. New Product Development & Product Life Cycle : New Product Development Process: Idea Generation to commercialization. Product Life Cycle : Concept & Characteristics of Product Life Cycle. Relevance of PLC and Strategies across stages of the PLC. Branding: Introduction to Branding, Product Vs. Brand, Meaning of a brand, brand equity & brand elements. Packaging & Labeling : Meaning & role of Packaging & Labeling, Pricing Basics: Meaning, Importance and Factors Influencing pricing decisions. Setting the Price : Setting pricing objectives, Determining demand, Estimating costs, Analyzing competitors’ pricing, Selecting pricing method, Pricing approaches
9
8 04
Place: The Role of Marketing Channels: Channel functions & flows, channel levels. Channel Design Decisions: Analyzing customers’ desired service output levels, establishing objectives & constraints, Identifying & evaluating major channel alternatives. Channel Options: Introduction to Wholesaling, Retailing, Franchising, Direct marketing, E-Commerce Marketing Practices. Logistics Decisions: Order processing, Warehousing, Inventory, and Transportation. Promotion: The role of marketing communications in marketing effort. Communication Mix Elements : Introduction to Advertising, Sales Promotion, Personal Selling, Public Relations, Direct Marketing, Concept of Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC)
05
Marketing Planning & Control : Product Level Planning : Preparation & evaluation of a product level marketing plan, Nature & contents of Marketing Plans – Executive Summary, Situation Analysis, Marketing Strategy, Financials, Control. Contemporary topics: Viral marketing, Guerrilla marketing, societal marketing, Relationship marketing, green marketing, digital marketing, ( Concept only)
Reference Books Marketing: Baines, Fill and Page , Sinha , Oxford Marketing Management – Kotler, Keller, Koshy, Jha, Pearson, Marketing by Lamb Hair Sharma, Mc Daniel Cengage Learning Marketing Management, Ramaswamy & Namakumari, McGrawHill Marketing Management – K Karunakaran, Himalaya Publishing House Marketing Management – Text and Cases, Tapan K Panda, Excel Books Marketing Management Concept & Cases – S.A. Sherlekar Marketing Management – Karunakaran Marketing Management - Bose
7
Code : MNG 103 FINANCIAL ING AND ANALYSIS Credit- 4 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1. To familiarize the students with ing principles and acquaint them with ing mechanisms, process and systems so as to develop their skills of preparing financial statements. 2. To develop their ability to read annual reports and develop their skills to interpret financial statements. 3. To familiarize the students with different financial ing concepts affecting stakeholders Unit
Contents
01
Class Hours 6
Introduction to ing: What is ing? The need for ing, External and Internal End s of ing Information, ing concepts and conventions, ing cycle, ing Equations, Nature of GAAP, Need for ing Standards, Limitations of ing, Ethical Issues in ing, Basic Terminologies of ing. 8
02 Mechanics of ing: Introduction, Classification, Double Entry System, Preparing Journal, Subsidiary books, Ledger, preparation of Trial Balance. Preparation of Income statement and Balance Sheet.
03
(The students should familiarize with computerized ing and should be able to do a task relating to above through a software package). Corporate s: Share and Share Capital, Issue of Shares, Payment in installment, Buyback of shares, Debentures and Bonds. Understanding corporate Income statement and Balance Sheet as presented in the Annual Reports of companies.
8
04
Analysis and interpretation of Financing Statements:- Common size statement, Trend analysis, Ratio Analysis and Cash Flow Analysis as per AS – 3 (Revised).
8
05
The faculty has to pick up Annual Reports of at least 5 listed companies from different sectors and make groups to analyze the following aspects : - Financial analysis as reported by Auditors and Directors’ and Corporate Governance. - Basic EPS and Diluted EPS as per AS – 20 - State of Affairs through Valuation Ratios and Dupont analysis.
10
-
Consolidated statements of Cash Flows from the perspectives of lender, investor, Prospective employee and supplier to the company. Corporate disclosures in the Financial Statements and Annual Reports of past 5 years. Innovative Techniques of FSA
Reference Books Financial ing for Management; Paresh Shah, Oxford Financial ing A managerial Perspective-Bapat & Raitha, McGrawHill Financial ing for Managers-Sanjay Dhamija, Pearson Financial ing and Analysis- Athma, HPH Financial ing for Management, A.K.Bhattacharya Financial ing for Management, Narayanswamy
Code: MNG - 104 ECONOMICS FOR MANAGEMENT Credit – 4 Class Hours: 40 Objectives: 1. To lay an adequate theoretical foundation to study various applied fields in economics and management. 2. To demonstrate the application of economic theory to business decisions. 3. To develop a student’s ability to think analytically about the economic forces at work in society. 4. To develop a framework which the students may use to analyze the overall behavior of a modern mixed economy. Unit 01
02
Contents
Class hours. Relevance of economics for business decisions, Role of Managerial Economist 8 and Business decision making. Demand Analysis – individual market and firm demand, Determinants of demand, Elasticity measures and business decision making, Demand Estimation and demand Forecasting, Supply Analysis. Production functions: Single variable – Variable Proportions, two variables – isoquants, returns to scale; cost minimization and output maximization, Elasticity of substitution various cost concepts, cost functions and their empirical estimation, Economics of scale and economies of scope (simple numerical problems to be solved).
8
03
Market morphology, price and output determination under different market conditions: Perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, Descriptive pricing approaches: Full cost pricing, product pricing; Price skimming, penetration pricing, loss leader pricing, price bundling, Transfer pricing (simple numerical problems to be solved).
8
04
Macro economics, circular flow of income, the concepts of GDP, GNP, GDP deflator, concepts of consumption, saving, and investment, business cycle: Nature, phases, consequences and measures to solve the problems of business cycle. Inflation. Inter sectoral linkages, Macro aggregates and policy interrelation ships: Fiscal and Monetary Policies; Industrial Finance: Money market, Capital Market and institutional finance.
8
05
8
Reference Books Managerial Economics, Geetika, Ghosh, Raychoudhury, TMH Managerial Economics, Salvatre, Srivastava, Oxford Managerial Economics, Keat, Young, Banerjee, Pearson, Managerial Economics – Analysis of Managerial Decision Making, H L Ahuja, S. Chand Managerial Economics Theory and Applications, DM Mithani HPH Managerial Economics, PL Mehta Sultanchand & Co. Managerial Economics, DN. Dwivedi, Vikash
Code: MNG-105 MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICES Credit- 3 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1. 2. 3. 4.
To explain the various concepts of management. To make the students understand the contemporary management practices To highlight professional challenges that managers face in various organization To enable the students to appreciate the emerging ideas and practices in the field of management.
Unit Contents 01
Class Hours
Introduction to Principles of Management 10
02
03
04 05
Basic Concepts : Definition of Management, Contribution of F.W. Taylor, Henri Fayol, Elton Mayo, Mary Parker Follet, Rensis Limert, Chestard Bernard, Douglas McGergor, Peter Drucker, Michael Porter and C.K. Prahlad. Approaches to Management : Scientific Approach, Systems Approach and Contingency Approach. Managerial Competencies : Communication, Team work, Planning and istrative, Strategic and Global Competencies. Organization : Formal and Informal, Line and Staff Relationship, Centralization Vs. Decentralization, Basic issues in Organizing, Work Specialization, Chain of Common Delegation, Span of Management, Organization Structure – Bases for Departmentation. Organizational Culture : Cultural Diversity, Multi Ethnic Workforce Organizing Knowledge Resource. Planning : Nature & Elements of Planning, Planning Types and Models, Planning in Learning Organizations, Types, Steps, MBO, MBE, Planning Premises. Decision Making : Risk and Uncertainty, Decision Trees, Decision making process, Models of Decision Making, Increasing Participation in Decision making, Decision-making creativity. Controlling : Process, Standards and Bench Marking – Co-ordinationPrinciples of Co-ordination-Inter-Dependence. Challenges in Management : Change Management – Timing of Change-Reaction to change-Planning organizational ChangeTechnological Change-Effective use of Communication Devices and IT.
10
8
5 7
Reference Books 1. Management, Robbins, Coulter & Vohra, Pearson. 2. Management: Text and Cases-VSP Rao, Excel Books 3. Essentials of Management-Koontz, 8/e, McGraw Hill 4. Management Theory & practice – Chandan J. S, Vikas Publishing House. 5. Management Theory & Practice Text & Cases – Subba Rao P & Hima Bindu, Himalaya Publication.
Code: MNG -106 ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOUR Credit- 3 Class Hours - 40 Objectives: 1.
To develop an understanding of the behavior of individuals and groups inside organizations To enhance skills in understanding and appreciating individuals, interpersonal, and group process for increased effectiveness both within and outside of organizations. To develop theoretical and practical insights and problem-solving capabilities for effectively managing the organizational processes.
2. 3.
Unit
Contents
Class Hours
01
Fundamentals of OB: Definition, scope and importance of OB, Relationship between OB and the individual, Evolution of OB, Theoretical framework (cognitive), behavioristic and social cognitive), Limitations of OB.
6
02
Attitude: Importance of attitude in an organization, Right Attitude, Components of attitude, Relationship between behavior and attitude, Developing Emotional intelligence at the workplace, Job attitude, Barriers to changing attitudes.
10
Personality and values: Definition and importance of Personality for performance, The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator and The Big Five personality model, Significant personality traits suitable to the workplace (personality and job – fit theory), Personality Tests and their practical applications. Perception: Meaning and concept of perception, Factors influencing perception, Selective perception, Attribution theory, Perceptual process, Social perception (stereotyping and halo effect). Motivation: Definition & Concept of Motive & Motivation, The Content Theories of Motivation (Maslow’s Need Hierarchy & Herzberg’s Two Factor model Theory), The Process Theories (Vroom’s expectancy Theory & Porter Lawler model), Contemporary Theories – Equity Theory of Work Motivation.
03
Foundations of Group Behavior: The Meaning of Group & Group behavior & Group Dynamics, Types of Groups, The Five – Stage Model of Group Development. Managing Teams: Why Work Teams, Work Teams in Organization, Developing Work Teams, Team Effectiveness & Team Building.
9
Leadership: Concept of Leadership, Styles of Leadership, Trait Approach Contingency Leadership Approach, Contemporary leadership, Meaning and significance of contemporary leadership, Concept of transformations leadership, Contemporary theories of leadership, Success stories of today’s Global and Indian leaders.
04
Organizational Culture : Meaning & Definition of Organizational Culture, creating & Sustaining Organizational Culture, Types of Culture (Strong vs. Weak Culture, Soft Vs. Hard Culture & Formal vs. Informal Culture), Creating Positive Organizational Culture, Concept of Workplace Spirituality.
05
Organizational Change : Meaning, Definition & Nature of Organizational Change, Types of Organizational Change, Forces that acts as stimulants to change. Implementing Organizational Change : How to overcome the Resistance to Change, Approaches to managing Organizational Change, Kurt Lewin’s-Three step model, Seven Stage model of Change & Kotter’s Eight-Step plan for Implementing Change, Leading the Change Process, Facilitating Change, Dealing with Individual & Group Resistance, Intervention Strategies for Facilitating Organizational Change, Methods of Implementing Organizational Change, Developing a Learning Organization.
Reference Books 1. Understanding Organizational Behaviour, Parek, Oxford 2. Organizational Behaviour, Robbins, Judge, Sanghi, Pearson. 3. Organizational Behaviour, K. Awathappa,HPH. 4. Organizational Behaviour, VSP Rao, Excel 5..Introduction to Organizational Behaviour, Moorhead, Griffin, Cengage. 6. Organizational Behaviour, Hitt, Miller, Colella, Wiley
8
7
Code: MNG -107 ENGLISH COMMUNICATION SKILLS Credit- 3 Class Hours - 30 Objectives: 1. To develop the communication skills of the students 2. To encourage the students to make correct usage of English with an emphasis on Listening, Speaking, Reading and Writing skills 3. To familiarize the students with professional communication. Unit
01
Contents
Basics of Communication
Class Hours 6
Importance of communication ,Communication elements and process, General communication and business communication, Information Gap principle, Turn-taking, Awareness of Filters & Barriers & Strategies for overcoming them, Verbal and non‐verbal communication, Principles of effective communication, Communication network in an organization Communication through English 02
6 The importance of communication through English at the present time, Plain English. Bias free English, Formal / Informal language use in appropriate contexts. The Sounds of English: Vowels and consonants, IPA symbols, Syllables, Stress and Intonation.
03
Major Language Skills (LSRW) Listening: Importance, Active & ive listening, barriers, strategies for improving listening skills. Speaking: Characteristics of Effective Speech-Clear articulation; Rate of speaking; Voice quality; Eye ; Relevance of content for the audience Reading: D e v e l o p i n g reading skills of skimming and scanning; predicting, guessing the meaning of unfamiliar words, inferring; reading critically, taking notes. Writing: the characteristics of effective writing, clear organization and structuring of ideas, summarizing, clarity of language, stylistic variation, précis writing, paragraph writing.
6
04
05
Functional English Grammar English Verbs, Tenses, Subject-verb concord, Negation, Interrogation Parallel structure, Modifiers, Clause and its types, Punctuation.
6
Conversations, Dialogues and Debates: Purpose and features of good conversations, tips for improving conversations, situational dialogues and role plays, Features of a good debate and how to prepare for it.
6
Reference Books 1.Communication Skills , Sanjay Kumar & Pushpa Lata, Oxford 2.An introduction to Professional English and Soft Skills: Das et al, BPUT Text Book. CUP. 3.Better English Pronunciation, J.D.O. Connor (Cambridge) 4.A University Grammar of English, Quirk et al, Pearson 5.Business communication, C.S.G. Krishnamacharyulu & Lalitha Ramakrishnan
Code: MNG -108 ENGLISH COMMUNICATION SKILLS - LAB Credit- 2 Class Hours - 20 1. 2. 3.
4.
Role plays for practice in effective use of body language, paralanguage and spatial communication. Phonemic transcription using IPA symbols. Syllable division and stress marking Listening exercises Listening with a focus on pronunciation: segmental sounds, stress, weak forms, intonation. Listening for meaning: listening to a short talk / news bulletin. Taking notes from a lecture/speech. Speaking exercises
5.
Pronunciation practice (for accent neutralization), Practicing word stress, and intonation. Practice of greetings and other functional expressions. Giving a short speech on a topic of interest. Participate in debates. Reading exercises Note making after reading a text, showing the main idea and s upporting ideas and the relationship between them.
6.
Writing exercises Practice in writing paragraphs , Précis writing
7.
Practice exercises on the common grammatical errors. Remedial measures to focus on correct use of English verbs, sentence structures, clause-types, Interrogation and parallel structures.
Lab Tests: 1st Lab test, 30 marks.(Listening, Speaking, Non-verbal communication) 2nd Lab test, 40 marks (Reading, Pronunciation, Grammar & Vocabulary) 3rd Lab test 30 marks (Writing) Suggested Readings: 1. A practical Course in Spoken English, Gangal, PHI 2. English Language Laboratories, Nira Konar, PHI
MBA Structure (Choice Based Credit System) EFFECTIVE FROM 2015-16 1st Year MBA 1st Semester Code No.
Subjects
Credit
University Marks
Internal
Total Marks
MNG 101 MNG 102
Statistics and Decision Science Marketing Management
4 4
100 100
50 50
150 150
MNG 103
Financial ing and Analysis
4
100
50
150
MNG 104
Economics for Management
4
100
50
150
MNG 105
Management Principles and Practices
3
100
50
150
MNG 106
Organizational Behaviour
3
100
50
150
MNG 107
English Communication Skills
3
100
50
150
MNG 108
ECS Lab
2
-
100
100
27
700
450
1150
Credit
University Marks
Internal
Total Marks
Total
2nd Semester Code No.
Subjects
MNG 201
Business Research Methods
3
100
50
150
MNG 202
Business, Environment and Society
3
100
50
150
MNG 203
Financial Management
4
100
50
150
MNG 204
Banking and Insurance
3
100
50
150
MNG 205
Operations Management
4
100
50
150
MNG 206
Human Resource Management
4
100
50
150
MNG 207
Managerial Communication
2
100
50
150
MNG 208
Managerial Communications Skill Lab
2
-
100
100
MNG 209
Business Data Analysis Lab
2
-
100
100
27
700
550
1250
Total
Summer Vacation: Summer Training Program for 4 to 8 weeks in identified sector.
2nd Year MBA 3rd Semester Code No.
Subjects
Credit
University Marks
Internal
Total Marks
MNG 301
Cost and Management ing
3
100
50
150
MNG 302
Business Law
3
100
50
150
MNG 303
Start ups and Business Incubation
3
100
50
150
MNG 304
Elective-I (Major)
4
100
50
150
MNG 305
Elective-II (Major)
4
100
50
150
MNG 306
Elective-III (Major)
4
100
50
150
MNG 307
Elective-IV (Minor)
4
100
50
150
MNG 308
Summer Internship
3
100
-
100
28
800
350
1150
Credit
University Marks
Internal
Total Marks
Total
4th Semester Code No.
Subjects
MNG 401
Strategic Management
3
100
50
150
MNG 402
Elective-V (Major)
4
100
50
150
MNG 403
Elective-VI (Minor)
4
100
50
150
MNG 404
Open Elective
3
100
50
150
MNG 405
Project Work on Business Management
4
-
100
100
18
400
300
700
Total
Each student shall undergo a project work in a business enterprise for 2 months during 4th Semester.
Detailed Syllabus for 2nd Semester, MBA MNG-201 BUSINESS RESEARCH METHODS Credit-3 Class Hours-40 Objectives: To equip the students with the basic understanding of the research methodology in changing business scenario. to provide an insight into the application of dynamic analytical techniques to face the stormy challenges, aimed at fulfilling the objective of business decision making. Unit Contents Class Hours Introduction to BRM: 01 Meaning and significance of research. Importance of scientific research in business decision making. 8 Types of research and research process. Identification of research problem and formulation of hypothesis. Research Designs. Measurement and Data Collection. 02 Primary data Secondary data 8 Design of questionnaire Sampling fundamentals and sample designs. Measurement and Scaling Techniques Data Processing Data Analysis – I: 03 Hypothesis testing Z-test, t-test,F-test, chi-square test. 12 Analysis of variance. Non-parametric Test – Sign Test, Run test, Krushall – Wallis test Data Analysis – II: 04 Factor analysis. Multiple Regressions Analysis. 12 Discriminant Analysis (Concept) Report writing and presentation: Research Report, Types and significance Structure of research report Presentation of report. 05 Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory Practical Aspect : Students are expected to use the 40 days trial version of relevant software package to learn the following :-
(I) Draw frequencies, bar charts, histogram. (ii) Creating and editing graphs and charts. (iii) Bi-variate correlation. (iv) The t-test procedure. (v) Non-parametric Tests : Chi-square Test. (vi) One way ANOVA Procedure. (vii) Simple Regression, Multiple Regression, Reliability Analysis, Factor Analysis. Reference Books: 1. Research Methodology, by Deepak Chawla / Neena Sandhi (Vikas) 2. BRM by Zikmund / Babin / Carr / Adhikari / Griffin (Cengage) 3. Research Methodology, by V. Upadade &A. Shende (S. Chand) 4. Business Research Methods by Naval Bajpai, Person 5. Business Research Method by Cooper et.al, McGraw Hill 6. Research Methodology by Khatua and Majhi, HPH.
MNG 202 BUSINESS, ENVIRONMENT & SOCIETY Credit-3 Class Hours-30 Objectives: 1. To analyse different issues of environment and measures to control those. 2. To enrich the students’ understanding of current scenario of society and related problems. 3. To direct the attention of students towards activities meant for betterment of the society. 4. To make the students understand the initiatives of corporates to pay back to the society and how they derive a social return in long run. Unit Contents Class Hours Concept of business environment: 01 Business Environment : Classification (Internal; External :- Micro &Macro 7 – Economic, Political-legal, Socio-Cultural, Techical, Democraphic, Natural International), Technics of Analysis and Diagnosis ((SWOT, ETOP, Forcasting; The New Economic Policy (LPG); National and State Level Industrial Polices. Environmental Issues and Controlling Measures: 02 Cause, effect and control measures of pollution (Air, Water, Soil, Marine, 7 Noise, Nuclear hazzards); Cause, effect and control measures of urban and industrial wastes; Managing Natural Disasters (flood, earthquake, cyclone and landslides) and Man made Disasters. Contemporary Social issues: 03 Polpulation explosion; Poverty-cause, effect and control measures; 7 Unemployment; Dowry, Domestic violance; Child labour; Terrorism; Cyber crime; Corruption in public sphere; Ineuality of caste and gender; Issues related to religious, ethnic, regional,minority, backward class, dalits in India. Corporate Social Responsibility(CSR): 04 Concept,Dimensions of CSR, Models of CSR: Philanthropic, Europian and Indian; CSR initiatives by public and private sector organizations in 9 India; Social audit; Social Return on Investment(SROI)- Concept, steps to measure, Implications, Community Welfare, Elevated Executives. 05 The above contents need to be discussed in the class room through field studies, case analysis and seminar presentations etc.
Reference Books: 1.Environmental Studies, Bosak, Pearson 2.Indian Social Problems- A Sociological Prespective, Rao CNS, S Chand 3..Social Problems in India, Ahuja R, Rawat Publishers 4. Environmental Studies, Asthana / Asthana – S. Chand
5. Environmental Management – Pandey Vikash Publication. 6. Business Ethics – Murthy Himalaya Puhlishing House 7.Business Environment, Paleri, Cengage MNG-203 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT CREDIT: 4 CLASS HOURS: 40 Objective :This course provides students with concepts, techniques and tools to study, analyze and improve their knowledge on financial management practices of an organization
Unit 01
02
03
04
Contents Foundations of Finance Nature &Scope. Organization of Financial Functions. Emerging role of FMs in India and in Global context. Financial Goal.Agency problems. Time value of money. Risk and Return concepts, Risk and return in a single asset and two assets portfolio. Investment Decisions. Capital Budgeting: Features, types and Techniques of capital budgeting decision. Cost of Capital. Financing &Dividend Decision: Operating Leverage, Financial Leverage. Capital structure. Theory and Policy. Sources of Long term finance, Dividend Theory.Dividend Policy. Current Assets Management: Working Capital concepts, Policies, estimation, factors affecting working capital, Sources of financing Working Capital, Management of cash : Cash budget, Management of collections and disbursement, Investment of Surplus cash ; Management of Receivables : of Credit, Credit Policy decision ; Management of Inventory : Techniques of Inventory planning and control.
05 Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory Books : 1. Essentials of Financial Management, IM Pandey, Vikas 2. Financial Management, Khan & Jain, McGraw Hill, 3. Financial Management, Srivastav & Misra, Oxford. 4. Financial Management, G Sudarsan Reddy, HPH 5. Financial Management, Kapil, Pearson 6. Financial Management – Tulsian (S Chand) 7. Fundamentals of Financial Management, Brigham, Cengage
Class Hours 10
10
10
10
MNG-204 BANKING AND INSURANCE Credit-3 Class Hours-30 Objectives: To equip students with a thorough understanding of need and importance of banking and insurance in the modern day life. To make students understand the basic legal provisions necessary for banks in India to operate. To summarize methods of handling risk, identify and explain features of insurance, its advantages and dis advantages. Unit Contents Class Hours Overview of Banking 01 Evolution of Banking, Structure andTypes of Banks (Commercial Bank, Cooperative Bank, Payment Bank, Small Banks), Roles of Banks (viz. 6 Intermediation),Payment system, Financial services), Banking Services, Banking Products – Deposit and Loan products, Payment products. EBanking, RTGS and NEFT. Banking Regulations and Financial Stability 02 Need and importance of Banking regulation in India, Banking Regulation Act,1949; KYC and AML guidelines, Banking Fraud, Banking Code, 7 BASEL norms, SARFAESI ACT, ARCs,Banking ombudsman scheme; policies with respect to priority sector and MSMEs. Basics of Insurance 03 Basic principles of business of insurance, Types of insurance: Life and Nonlife Insurance, Re Insurance. Principles governing marketing of 10 insurance products; Insurance regulations and role of IRDA. Extension of insurance to Niche areas: Pension plans, Bancassurance, ULIPs, TPA, Micro Insurance, Insurance Inclusion. Insurance Risk and Claims Management 04 Risk and Uncertainty, Risks associated with business of insurance i.e . pure risk, financial risk, fundamental risk. Classification of pure risk, 7 overlapping risks; Rules of Risk management, Risk management techniques, Risk management process, Underwriting. Claims settlement procedure for Life insurance, Motor insurance and HealthInsurance. 05
Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory
Reference Books: 1. Banking Theory, Law and Practice – Gordon – Natarajan, HPH 2. Banking and Insurance – Mohapatra and Acharya, Pearson 3. Insurance and Risk Management, P.K. Gupta – HPH 4. RISK Management and Insurance – Triechmann, Cengage
5. Banking Theory &Practice – Shekhar / Shekhar (Vikas) 6. Banking Law and Practice – S. Mishra (S Chand) 7. RBI Bulletin 2013, 2014 8. National Insurance Academy publications
MNG 205 OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Credit: 4 Class Hours-40 Objective: 1.
To understand the concepts, principles, problems, and practices of Operations Management.
2.
To understand the importance of an effective operations strategy in an organization.
3.
To understand the various production and operations design decisions and how they relate to the overall strategies of organizations.
Module
Contents
Overview of Operations Management– Operations in Manufacturing and Services, Responsibility of Operations Manager, Operations Strategy and Competitiveness, Process Analysis, Manufacturing Process and Service Process Selection and Design, Job Design and Work Measurement. Facility Location, Layout &Capacity Planning– Locational Factors, II Techniques; Factor Rating Method, Centroid Method; Facility Layout, Process Layout, Product Layout and Line Balancing, Fixed Position Layout, Service Operations Layout, Modern Layouts, Types of Capacity, Capacity Planning &Strategies, Economics of Scale and Scope. Aggregate Planning, Scheduling &Project Management– III Aggregate Planning; Relevant Cost and Strategies, Scheduling; Priority Rules and Techniques, Gantt Chart; JIT; Project Management, PERT/M- Network Diagram and Critical Path, Slack &Float. Quality Managementand Supply Chain Management– Concept of IV Supply Chain Management; Concept of Quality; Design of Quality Control System, Statistical Quality Control, Types of Control Chart – X Chart, R Chart, P Chart, TQM (Total Quality Management) Concepts, Introduction to ISO 9000 &14000 Standards. V Case Studies – Emphasis shall be laid on case studies and solving business related numerical problems in all the above modules. Reference Books:
Class Hours
I
10
10
10
10
1. Operations Management, Chase et.al – Tata McGraw Hill. 2 Operations Management, Meenakhi Kumari, Cengage 3. Production and Operations Management, Kaniska Bedi, OXFORD 4. Production and Operations Management, K. Aswathappa, K. Shridhar Bhat, HPH 5. Production &Operations Management, SP Singh, Vikas Publication 6. Operations Management, Heizer and Render, Pearson MNG-206 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Credit-4 Class Hours-40 Objectives: 1. To introduce and explain different phenomenon of Human Resource Management (HRM). 2. To enrich the students’ understanding on HRM , which may enable them to implement the concepts in the workplace. 3. To direct the attention of students towards some of the emerging concepts of HRM. Unit Contents Class Hours 01 Concept, Definitions and Objectives of Human Resource Management(HRM); Functions of HRM; Process of HRM; Evolution of HRM; Strategic HRM and its role in the organization; Human Resource 10 Planning(HRP):Meaning and Process, Job analysis: Job description and Job specification; Recruitment: Meaning, Sources, Process and Yield; Selection: Meaning and Process, Tests and Interviews, Induction and Socialization. 02 Performance Appraisal: Meaning, Objective, Process and Methods; Potential Appraisal; Biases in performance appraisal; Methods of job evaluation; Meaning of Compensation; Types of compensation; Types of 10 wages and theories; Wage differentials; Pay structure, Wage Law in India, Executive Compensation. 03 Concepts of Career, Career planning process, Career Stages; Training &Development: Concept, Training need analysis and Methods of training 10 (on-the-job and off-the-job training), Evaluation of Training effectiveness; Concepts of Promotion, Transfer and Separation. 04 Industrial Relations (IR): Concept and Approaches to IR, John T. Dunlop’s System Theory of IR, Positive and Negative IR, Role of State in IR; Trade Unions: Concept and Registration; Structure and Functions of Trade Union, International HRM: Definitions and Approaches, Concepts of Expatriate, Parent country National (PCN), Host Country National 10 (HCN)and Third Country National (TCN). Challenges of HRM in dynamic business environment; Ethical issues in HRM HR Outsourcing; Employee Engagement; Organization Citizenship Behaviour(OCB), Talent Management, Competency Mapping. 05 Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory
Reference Books: 1.HRM Text &Cases, Aswathappa,TMH. 2. Personnel &Human Resource Management, P.Subba Rao,HPH 3. Human Resource Management,Jyoyi,Venkates, Oxford 4. HR, Denisi and Sarkar, Cengage. 5. Human Resource Management (Seema Sanghi (Vikas) 6. Human Resource Management – S.S. Khanka – (S. Chand) 7. Human Resource Management – Dessler and Verkky, Pearson
MNG- 207 MANAGERIAL COMMUNICATION CREDIT - 2 CLASS HOURS: 30 Objectives: To develop the communication skills and soft skills of the students To enhance the ability of the students to participate in group discussions and personal interviews Unit Contents Class Hours 1
Introduction to Managerial Communication
7
1.1. Communication challenges in today’s work place: Advances in technology; Culturally diverse workforce; Team-based organizational Settings. 1.2 Effective Business Presentations: Importance in managerial communication; Planning, Preparing, Organizing, Rehearsing, and Delivering Oral presentations, Handling Questions; Power Point Presentation 2
Introduction to Managerial writing
7
2.1. Business letters: routine and persuasive letters, bad news letters, sales letters, job application letters. 2.2. Writing CVs. 2.3. Memos, notices, circulars, emails. 2.4 Business reports and proposals. 3
Group Communication 3.1. Business Meeting: Planning a meeting; Drafting a Notice-cumAgenda; Role of the Chairperson and other participants; preparing the
8
Minutes of a meeting. 3.2. Group discussion: Types; Do's and Don'ts of GD; Guidelines for Effective Group Discussions.. 3.3Types of managerial speeches: Speech of Introduction, speech of thanks, occasional speech, and theme speech. 4
Soft Skills
8
4.1. Communication skills and Soft Skills. 4.2. Mastering the art of giving interviews, Types of interviews, Planning and Preparing for a Job Interview; Frequently Asked Questions in a Job Interview; Stages of an Interview; Important Nonverbal Aspects; Strategies for success in Job Interviews. 4.3. Business and social etiquettes. 5
Case analysis and self study assignments are compulsory
Recommended Books: 1. Business Communication- concepts, cases & applications,Chaturvedi & Chaturvedi,
Pearson
2. Business Communication, Meenakshi Raman & Prakash Singh, Oxford 3. Communication for Management, Urmila Rai and S M Rai, HPH 4. Business and Managerial Communication, Sengupta, PHI 5. Business Communication for Managers, P. Mehra, Pearson 6. BCOM 2nd Edition, Lehman and Sinha, Cengage 7. Soft Skills K Alex, S Chand 8. Business Communication, Kalia and Agarwal, Wiley
Managerial Communication Skills (Lab) Credit – 2 Hours - 30 Unit
Contents
1
Managerial Writing: Business letters, ment, Preparing Press Releases, Press Notes, Writing themespeeches, Speeches of thanks.
2
Group Team / Communications: Preparing for GDs, Interviews, Writing CVs and Resumes, Internal communications for employee engagement.
Sessions (in Hours) 6 12
Business Etiquette. 3
4.
Corporate Communications: Notices, Agenda, Board Room Behaviour, Minutes, Exercises in Corporate writing, Preparing Presentation, Making presentations before the top management.
6
Learning Emotional Skills: Emotional Skills and your personality, Interpersonal relations. Know your EQ. EQ Tests.
6
30 Hours Conducting Tests : 1.
There shall be two lab tests carrying 30 marks each and another carrying 40 marks.
2.
The faculty concerned shall design the tests on topics prescribed in the syllabus.
Recommended Books : 1.
English Language Lab, Nira Kanor, PHI
2.
Guide to Managerial Communication, Mary Munter, Pearson
3.
Cengage Learning India, English Language Communication Skill – Lab Manual
4.
Soft Skills for Everyone, Butterfield, Cengage
5.
Campus to corporates, Sage Publication
Conducting Tests: 1.
There shall be two lab tests carrying 30 marks each and another carrying 40 marks.
2.
The faculty concerned shall design the tests on topics prescribed in the syllabus.
Recommended Books: 1. English Language Lab, Nira Kanor, PHI 2. Guide to managerial Communication, Mary Munter, Pearson 3. Cengage Learning India, English Language Communication Skill – Lab manual 4. Soft Skills for every everyone, Butterfield, Cengage
MNG 209 Business Data Analysis Laboratory
Credit: 2 Hours : 30 Teaching Scheme: Laboratory 4Hrs/Week Prerequisites: Basic Mathematics and Management Objective:To Make students familiar with business data analysis,retrieval using computer for research and report generation. Session 1
Contents An introduction to creating and formatting worksheets
Hours 2
The session includes : Insert and delete worksheets;Copy, reposition, copy and move, rename, grouping and applying coloring to worksheet tabs 2
Applying formulas and functions
4
Create formulas This session includes :
Use of basic operators
Revision of formulas
Enforce precedence of operation This session includes:
3
order of evaluation
precedence using parentheses
Precedence of operators for percent vs exponential
Apply cell reference in formulas
2
This session includes:
4
Relative
Absolute
Applying conditional logic in a formula This session includes:
Create formula with values that match your conditions
Edit defined conditions in a formula
Use a series of conditional logic values in a formula
2
5
Apply name ranges in a formulas.
2
This session includes: 6
Define,edit and rename a named range
Apply cell ranges in formulas.
2
This session includes :
7
Enter a cell range destination in the formula bar
Define a cell range using the mouse
Define a cell range using a keyboard shortcut
Presenting Data Visually
2
This session includes :
Create charts based on worksheet data. Introduction to Query Language
8
4
SQL DDL commands This session includes:
Creating tables
Creating table with constraints
Altering tables
SQL DML commands This session includes
Inserting data into tables
Updating data into tables
Deleting data from tables
9
Getting data using Query Use of select statement to create data queries
2
10
Advance Query 1
4
Use of SQL functions (aggregate functions,group functions etc.) Advance Query 2
Use of s and sub queries
11
Lab. Test 1 (Spread sheet - 50 marks)
2
12
Lab. Test 2 (Query language - 50 marks)
2
Total no. of Lab Hours = 30
Note: Lab activities will be done using only open source spread sheet and open source database like My SQL Course Outcome: After taking this course the student will be able to:
Design spreadsheets and data base tables for data analysis
Analyse the data and prepare graphical reports